
Should Age or Need Be The Basis for Entitlement?
Should Age or Need Be The Basis for Entitlement?
I. Financial status of the elderly:
Percent of People 65 Years and Over Below Poverty Level in the Past
12 Months: 2006 (new census data not yet available)
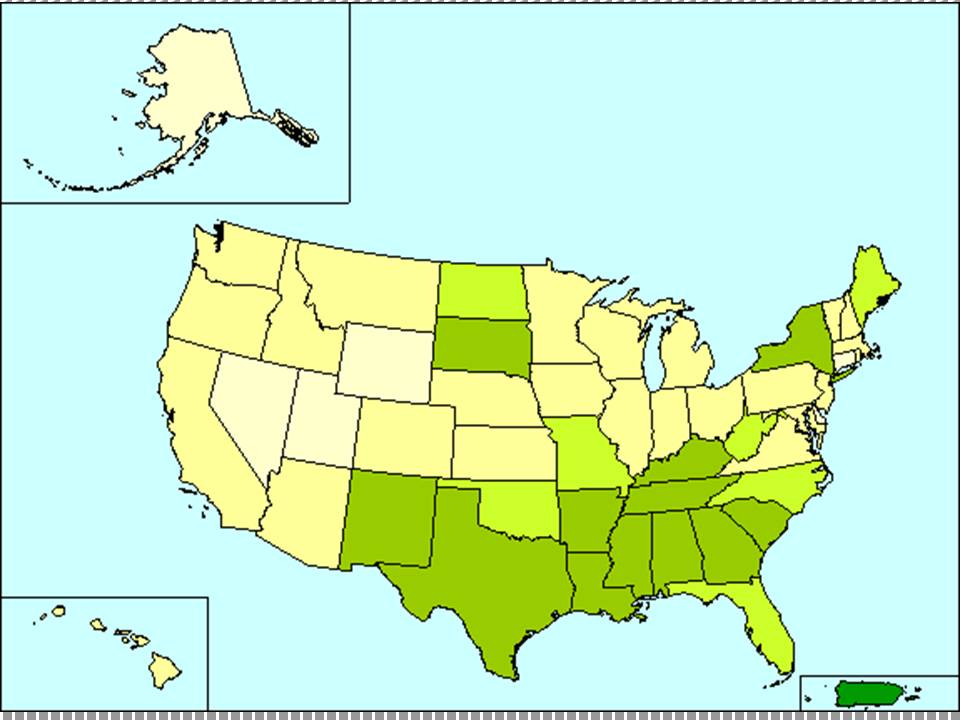
Poverty rates for people over age 65 declined from nearly 35% in 1959 to an average of 10.2% in 2002. But as the chart above shows, not for everyone. Because of Social Security, automatic cost of living adjustments ( referred to as COLA's) and because women now pay into the Social Security system, and thus have a pension in old age, the extent of poverty among the elderly is less than the rest of the population.
It is important to note that the poverty rate among children also declined after 1959, through the early seventies. Recently has swung up sharply again to 20.6 percent in 1990 and remains higher than the poverty rates among other age groups. The rise of female headed households and the disparity between women's and men's wages has been cited as a major cause. The phenomenon has been called the feminization of poverty.
If we were in a face to face class I would ask how many of you who live alone could live on less than $10,000 a year?
The poverty rate was historically set by estimating the cost of a minimally adequate food budget and multiplying by 3. Three was used because research from the 1950ís suggested that American's spent about 1/3 of their income on food. To most people this income is inadequate to have a full life .
Women and Poverty - Women have a higher rate of poverty than men. It is often said that aging ins a woman's issue because women live longer, are at a higher risk of being poor and are more likely to outlive their resources. Read this article.
Health care costs further complicate life for nearly poor elders because for many, as we age, there is an increased need for health care. Marginally poor can spend up to 1/3 of their income in direct out of pocket expenses for health care. Without Social Security it is estimated that nearly 50% of seniors would fall below the poverty line.
Poverty rates reflected as below poverty level by race.
- 1 in 12 whites (8.3%)
- 1 in 5 Hispanics (18.8%)
- 22.3% of African Americans
If you are interesting in further readings this is a very interesting site regarding the face of poverty in this country.
http://money.cnn.com/news/specials/poverty/
II.
Needs Based Program vs. Entitlements Needs Based
Programs
"means
testing".
Usually, social programs that are needs based qualify people based on some criteria, usually income. To qualify for a needs based
program the person must be at the federal poverty guideline for low
income. This is often referred to as
Some examples of needs based, social programs, are Supplemental Security Income (SSI- paid to the elderly whose Social Security benefit does not reach poverty guidelines), Medi-Cal, In-Home Support Services (IHSS- provides a chore worker to help with ADL's -Activities of Daily Living), and many subsidized housing programs). The old system of welfare was a needs based program. That is, it was only available for people with low incomes.
Entitlement
Programs :
are
programs based on benefits earned and not on income. Once you reach a
certain land mark (i.e. age, years worked, citizenship etc.) you are
entitled to the benefit regardless of your income.
Some examples of entitlement programs are: Social Security, Medicare, senior meals program, and Older Americanís Act programs (OAA) (even though OAA tries to target low income, one does not need to be low income to benefit from services such as dial a ride, home delivered meals
, or friendly visitor).Some argue that Social Security should be changed to a needs based program. Did you know that even the richest CEO's in the U. S., including the President are entitled to Social Security at the appropriate age? The Social Security articles in next week's readings will address this issue further. Read the argument, see what your opinions are. Someday, you may be asked to suggest policy. Where will you stand?
III. Expansion of Entitlements:
After WWII, there was a stark contrast between the affluent society, who were then called the working class, and the elderly population . The affluent had unions, pensions, and benefits. They bought the first suburban homes, TV's, and washing machines. But there were income problems among older people.
Do
you know how inflation is calculated?
The
Consumer Price Index is an index that documents increases or decreases
in the price you and I pay for goods. As it rises or falls inflation is
said to increase or decrease.
There is a list of over 100 items that the government checks monthly for price
changes. If the total purchase price of
those items is higher than they were the previous month inflation is
said to have occurred. If however, the prices are lower, deflation has
occurred. These numbers are also used to adjust Social
Security's cost of living adjustments or COLAS.
After WWII entitlements were seen as a necessary consequence of industrialization and economic growth . We had to take care of our rising poor.
It was not until
the end of the 1960's in the shadow of the View Nam war, that the economic growth
prompted Americans to improve the status further of older
Americans.
Social Security expansion
The financial status of the elderly improved with the advent of Social
Security (1935) and post WWII pension programs. We'll study more about pensions in the chapter on retirement.In 1971 the Advisory Council on Social Security reported that the program was over funded. It predicted that the fund would produce a $1 trillion reserve by 2025 (check out the dependency ratio during this period below).
he ratio of workers to beneficiaries for Social Security was 15 to 1 in the 1950's (it was around 19 to 1 at the time Social Security was instituted). That is, 15 people were working and paying taxes for each person drawing benefits.
DID YOU KNOW?
T
As the elderly population increases, the dependency ration is expected to increase too. In 1960 the ratio dropped to just 5 workers for each beneficiary. By 2034 that ratio is expected to be just 2 workers to each beneficiary.
These data are based on birth rates from 1964-1974 when we experienced a drop in birth rates.
Also, this is an influential voice in the debate on how population aging will affect public financing in years to come.
Do you know what happened to birth rates from 1977-1997? Click here to read from another week's lecture.
This author assumes that Social Security adds to the National Debt? Does it? You will see later on in this class that Social Security actually helps fund the Federal government. Check it out here http://www.ustreas.gov/press/releases/po3622.htm
Consider how this information might change your view of the solvency of Social Security.
That same year, the White House Council on Aging was documenting the inadequate wages of older adults. Remember also that Social Security had no inflation protection during this time. Increases in benefits were done periodically and only through changes in the law so the value of benefits was eroding.
President Nixon and Congress recommended that automatic benefit increases be instituted to keep pace with price increases. They would index Social Security payments to the cost of living. That meant that every time the cost of living increased, (remember those market basket of goods?),Social Security benefits would increase also. In 1970 the Federal Government started increasing Social Security payments to match that increase. These were called Cost of Living Raises or COLAíS , and matching Social Security to this number is referred to as indexing.
Some say the move was based on the political vie for the old age vote, since older people vote in larger numbers than younger voters (http://factfinder.census.gov/jsp/saff/SAFFInfo.jsp?_pageId=tp16_government). But for what ever reasons, Congress increased benefits 20% and indexed benefits to inflation. This ensured older people that inflation would not erode the value of their benefits.
- Because Social Security is one of the few government programs where people received something tangible for their tax, public support for the program remains high.
- As a result, between 1950 & 1991 the poverty rate among the elderly dropped from over 52% to just 11%.
- Social Security helped reduce poverty but indexing social security to the rate of inflation improved the elder's financial status even more. Today, nearly 50% over the age of 65 would still be in poverty if not for Social Security.
IV. Social Security As an Insurance Concept:
- Social Security was originally understood by the public as an insurance plan. A pooled risk insurance program where workers pay premiums to ensure income in old age.
A. Taxes were seen as premiums or contributions and workers felt they had old age insurance accounts that they were paying into to provide income in old age.
There was a problem with the insurance concept however. Participation and benefits in insurance programs tend to be standardized according to age, sex, occupation etc. Social Security income is not. For example:
- There are no exceptions for workers in dangerous and physically demanding jobs who
face different risks than people in sedentary jobs.
- Also pooled risk results in some people receiving less protection. For example, groups
with shorter life expectancy receive benefits for less time, especially low income and black men.
- Women are said to receive a higher rate of return because they live longer and can
draw benefits for an extended period of time.
V. The Regan Years (1980ís):
In the 1980's the economy began to deteriorate and inflation rose. Social Security payments were driven upward each month to keep pace (remember COLAS). Not only did payments increase, but the number of recipients also increased as the numbers of people living into old age grew (the dependency ration changed).
- cut public service jobs
- decreased the food stamp program
- eliminated Social Security death benefits
- phased out Social Security benefits for older children of deceased workers
When he attempted to further cut Social Security (he proposed a 10% cut in benefits and a 31% cut in early retirement benefits, which means retiring before age 65) public interest groups who protect middle-class entitlements organized to fight the proposal.
- Regan's public approval rating dropped 16 points and 2 Republican Congressional seats were lost in
the next election.- Social Security became the sacred cow that politicians would dare not touch.
Social Security appealed to the middle-class and they wanted it protected. But the economy was in trouble. Neither program cuts nor high tax rates were popular. How was Regan to bring spending for government programs under control? For the first time in the U. S. a two tiered structure of programs developed that divided the poor from the working class.
1. means-testing welfare
2. universal entitlements.
check the definitions of these two options earlier in this lecture
Even democrats who generally favor social programs favored more means testing; they came to resent the welfare burden when their own earnings power was eroding.
Regan responded to the slow economy and low approval ratings with what he called "supply side economics" to stimulate the economy.
The idea was to cut taxes for industry and industry would, in turn, re-invest the money they saved into creating more jobs, thus stimulating the production of more jobs.
Instead, tax cuts for business created an even larger Federal budget deficit, as Federal spending continued on Regan's Star Wars program, and fewer resources were flowing into the government coffers ( remember, people are poorer and are not buying goods so no taxes were collected which are, even today, a major source of Government income).
Supply side economics was supposed to fix the eroding purchasing power of the middle-class. If more products were produced the middle class would benefit with more jobs and lower costs for the products they purchased ( remember supply and demand drives the cost of most goods). The middle-class also supported the program because it left social programs in place.
But tax cuts to businesses made things worse.
Business Week 3/26/84
. . . "entitlements have been indexed to COLAís
[cost of living allowances] but the cost of
such protection is proving to be a burden that the rest of the nation
can no longer carry. No lasting solution to the deficit crisis is
possible without tempering the explosive growth of Social Security and
Medicare"
Industry's response was not surprising given the fact that employers are required, by law, to match employees contributions to the Social Security fund. Not a word was mentioned in main stream media about the loss of Government revenues from business tax breaks.
- Because of the economic problems of the nation, less taxes were available to flow into the Social Security fund.
- On 11/5/82 Social Security had to borrow $581 Billion from its companion funds (Medicare) to pay benefits.
- Instead of portraying Social Security as a victim of a falling economy with tax breaks decreasing revenues, it now became known as the source of the budget deficit.
- Regan refused to consider cuts in defense spending and cuts in other social programs would only make minimal reductions so Social Security became the target.
Debate over the Social Security issue prevented Congress from acting because an election was near. The issue was halted for the 1982 election.
Regan appointed members to The National Commission on Social Security Reform. Conservatives who represented business, liberals who represented organized labor, and senior citizens reached a compromise.
- They would enact a 6 month cost of living delay (COLA)
- Tax the benefits for upper-income retirees
- Institute measures to curb early retirement
- reduce benefits to 70% by 2022 if a person retires before age 65
- increase the age of full benefits from age 65 to age 67
- create a bonus to defer retirement (if you work until age 70 you earn bonus points)
- lower the penalty for continuing work while receiving benefit
The idea of an insurance metaphor was now unmasked. There was no pooled risk.
- Social Security's success depended solely on the Government's ability to collect taxes and not on some actuarial criterion (charts that calculate risk and premiums for insurance companies).
- The fund added $67 billion to its reserves and reserves were expected to reach $6.9 trillion by 2015.
- This eliminated the crisis but generated uncertainty about Social Security's value as a source of wage protection.
- Program opponents began to reshape the image of Social Security as an intergenerational tax (young giving to the old) rather than an old age insurance program.
Intergenerational equity became the new attack
The attack originated in the business community whoís message was spread through an organization called Americans for Generational Equity (AGE)
VI. Generational Equity: Are senior programs funded at the expense of children's?
The attack of intergeneration conflict really first began in the business community in 1972 as a protest to a tax hike and benefit increase.
Fortune Magazine warned of a "Sorrowful lot of Baby Boomers who would be forced to support both its parent's retirement and their own".
- Business called Social Security a "redistribution scheme" and tried to convince workers that it
was just another tax.
- Because of cuts in other social programs by 1982, 23% of children were in poverty .
Reganomics had cut programs to millions of low income, single mothers. But businesses blamed
support for aged programs as the cause.
- The media blamed aging programs for the national debt (even though Social Security is self funded).
- Elders with political power were seen as greedy, and demanding programs at the expense of youth.
- AGE grew with support from the private sector ( banks, insurance companies, defense contracts
and health care corporations) .AGE was able to move its agenda into the main-stream political agenda. It published books, news articles, and advocated a decrease in non-means testing entitlements by cutting COLAS to 60% of the Consumer Price Index.
AGE was successful in getting Social Security benefits taxed for all recipients as a way to decrease funds flowing out of the system.
VII. Last thoughts from the author of your text Harry Moody
"One of the reasons why the government provides help is because certain groups have greater needs. Children as a group have done badly in recent years, through naturally it does not follow that older adults have caused this unfortunate state of affairs.
In pursuing a discussion about "age versus need" or "generational equity" there are two common misconceptions that need to be addressed. On the one hand, there is the mistaken belief that most older people are poor; on the other hand the equally mistaken belief that most old people are now affluent or well off. As you have seen not all older people are alike.
The economic strength and stability of a country( how rich or poor the country is) drives its social policy and to some extent its social values. Social Security is a prime example. Why? Because when the country was well off and the national debt was low we instituted a policy to care for our elders. We instituted COLA's so that their income would keep pace with inflation. Do we still want to have such a policy in today's economic climate? How would each of us deal with parents who fall below the poverty level? Nearly 50% of all elders would if not for Social Security.
Social Security COALS (cost of living adjustments) are not the cause of poverty among children. Nor is the increased costs of medical care for the elderly.
The basic reason for poverty in children is their parents unemployment or under employment, and the high number of female headed households with low incomes.
Economic prosperity and education are strongly associated. America must have workers capable of making informed decisions, learning new tasks, and following complex instructions. Public education must be strong enough to do that.
Blaming the elderly does not address the issues necessary for a national level policy.
Social Security is a retirement and disability program that workers pay for themselves. If not for old age benefits, many younger family members would be contributing to the support of their elderly family members.
back to top Remember to check the Assignment Link